What is Accounts Receivable? Definition of Accounts Receivable, Accounts Receivable Meaning
What is Accounts Receivable? Definition of Accounts Receivable, Accounts Receivable Meaning

This is fairly common practice adopted by companies for liquidity. Gross Unearned Revenues are the total receivables (open invoices) that are due to the company. This does not take into account a scenario where the customer may default. Keeping your accounts receivable up-to-date is crucial, but that’s not the only part of successfully managing your business’ accounting needs.
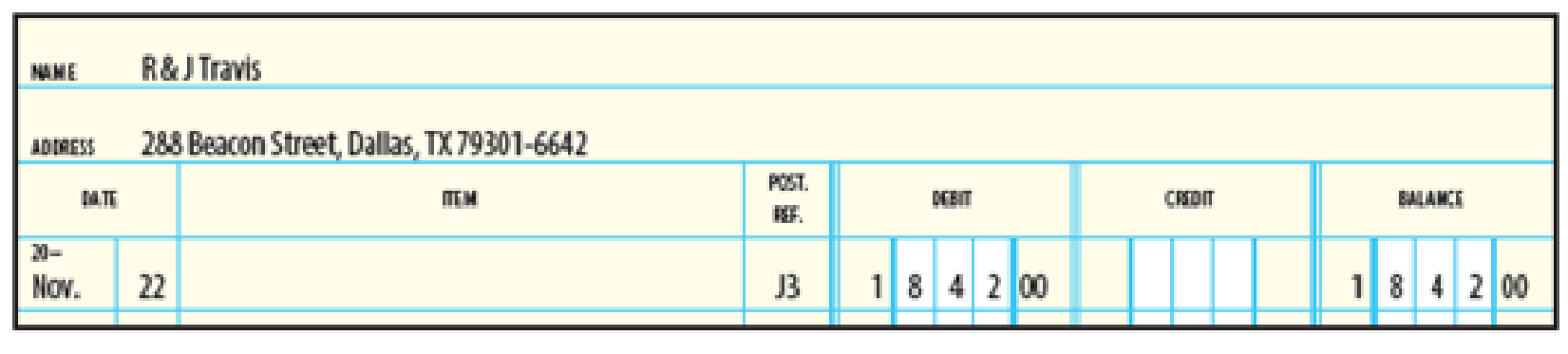
Generally, a company that sells products on credit sets terms for its A/R. The terms include the number of days within which customers must pay their bill before they are charged a late fee. When customers don’t adhere to the payment terms, the seller can approach its customer and offer new terms or some other remedy to collect on the bill. The best way to understand accounts receivable is to view a transaction and how it ends up on the balance sheet. Accounts receivable, sometimes shortened to “receivables” or A/R, represents money that is owed to a company by its customers for products or services that it has delivered but for which it has not yet received payment.
AccountingTools
Most companies allow for a portion of their sales to be on credit. Often, a business offers this credit to frequent or special customers who receive periodic invoices. This allows customers to avoid having to make payments as each transaction occurs.
The next step is to contact the customer or to move on with contacting a collections agency. It’s important to note that companies that sell on credit may not have an actual lien on the property. This means that the full amount on the property may not be collected. An asset management company that opts to bill in arrears, on the other hand, would temporarily have an A/R balance on its balance sheet, usually for only a day or two as fees are deducted from client custody accounts in most cases. An alternative method is the direct write-off method, where the seller only recognizes a bad debt expense when it can identify a specific invoice that will not be paid.
Accounts receivable is an important factor in a company’s working capital. If it’s too high, the company may be lax in collecting what’s owed too it and may soon be struggling to find the cash to pay the bills; if it’s too low, the company may be unwisely harming customer relationships or not offering competitive payment terms. In general, accounts receivable leciels correspond to changes in sales levels. When accounts receivable go down, this is considered a source of cash on the company’s cash flow statement, and as such, it increases the company’s working capital (defined as current assets minus current liabilities). When accounts receivable goes up, this is considered a use of cash on the company’s cash flow statement because the company is “stretching out” the time it takes to receive money owed to it and thus is using cash more quickly.
Notes receivable are written promissory notes that give the holder, or bearer, the right to receive the amount outlined in an agreement. Promissory notes are a written promise to pay cash to another party on or before a specified future date. If the note receivable is due within a year, then it is treated as What is the Accounting Equation a current asset on the balance sheet. Asset turnover is a ratio that measures the value of revenue generated by a business relative to its average total assets for a given fiscal or calendar year. It is an indicator of how efficient the company is using both the current and fixed assets to produce revenue.

You would think every company wants a flood of future, expected cash coming their way. However, money in A/R is money that’s not in the bank, which exposes the company to a degree of risk. If Wal-Mart went bankrupt or simply didn’t pay the publisher, it would be forced to write down the A/R balance on its balance sheet by $1.5 million. If no progress takes place, the accounts receivable balance is either turned over to a collection agency or, in more extreme cases, the firm sues the person or institution that owes it money, seeking relief from a court by seizing assets.
If the seller is operating under the cash basis of accounting, it only record transactions in its accounting records (which are then compiled into the financial statements) when cash is either paid or received. Since issuing an invoice does not involve any change in cash, there is no record of accounts receivable in the accounting records. Only when the customer pays does the seller record a sale. With the accrual accounting, you record a transaction whether cash has been received or not.
This can help you determine if an account is worth doing business with again. If the account has current liabilities, you should think twice about giving them credit that calendar year or in the near future. Having clearly stated payment terms in your service agreement is one of the most important steps in managing accounts receivable. Start with a 15-day payment deadline if possible, and extend the terms if asked by the customer over time.
- In other words, it’s money that a company has a right to receive because it has provided a product or service.
- An example of a common payment term is Net 30 days, which means that payment is due at the end of 30 days from the date of invoice.
- The money would still be owed, and the company would be out the money.
- So you probably won’t find anyone willing to buy your really old invoices.
- Company A is waiting to receive the money, so it records the bill in its accounts receivable column.
- However, there is always a business trade-off because delaying payment to vendors could tarnish the company’s reputation and could also result in missing out on early payment discounts.
The advantages and disadvantages of accepting credit cards for your small business
The Balance Sheet categorizes Account Receivables as a current asset because sales made on credit are expected to get paid soon as per the credit terms mentioned in the invoice issued by the seller. Sales made but not paid-for by the customers (trade debtors). Accounts receivables are shown as current (short-term) assets in a balance sheet and are, in fact, unsecured promises by customers to pay in the future.
A customer often receives some sort of product or service but has an amount of time, or a term, to pay the amount owed. The term, which is often 30, 60, or 90 days, provides some flexibility to the client, customer, or other company to pay it off.
If the payment was made on June 1 for a future month (for example, July) the debit would go to the asset account Prepaid Rent. Expenses normally have debit balances that are increased with a debit entry. Since expenses are usually increasing, think “debit” when expenses are incurred.
Accounts Receivables Examples of Industry
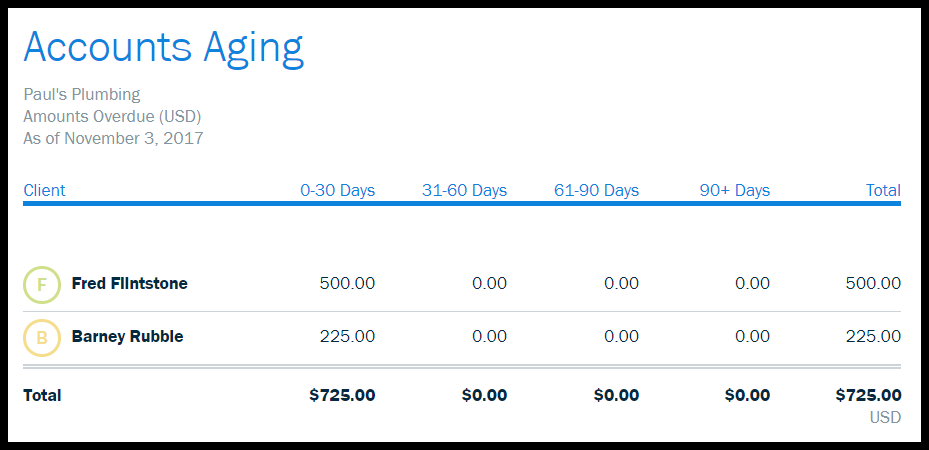
Accounts receivables is the amount that is due to the company by its customers. It is important to consider the default probability of the customer and therefore look at the Net Receivables numbers. Each industry has a different set of credit policy and hence, account receivable days differ by wide measures. There’s no getting around the fact that cash flow is a crucial element of overall financial performance. Managing your accounts receivable doesn’t just keep your business running smoothly.
The creditor may be able to charge late fees or interest if the amount is not paid by the due date. A manufacturer will record an account receivable when it delivers a truckload of goods to a customer https://www.bookstime.com/statement-of-retained-earnings on June 1 and the customer is allowed to pay in 30 days. From June 1 until the company receives the money, the company will have an account receivable (and the customer will have an account payable).
Equally, you may be interested in the accounts payable team, which manages the process of paying suppliers. The airline has booked the compensation in https://www.bookstime.com/ but hasn’t yet got the cash. Novo Nordisk’s finance function, which currently employs about 1,000 people, also might shed some jobs as part of a move to automate tasks including cash management and accounts receivable, Mr. Knudsen said. That would let People’s take steps to protect its collateral on WMG’s multimillion-dollar debt, in the form of machinery, equipment and inventory at the company’s Suffield headquarters, along with business records and accounts receivable.

Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!